No Products in the Cart
When encrypting emails, it’s important to encrypt all of them, not just the ones with sensitive information. If only some of your emails are encrypted, it is a red flag for a hacker and could make your inbox even less secure. They will only have to hack into a few emails rather than sift through hundreds to find data they can use. We explain how to encrypt emails on multiple providers and summarize our tips in aninfographic.
What is Email Encryption?
Email encryption is essentially mixing up the contents of an email so it becomes a puzzle that only you have the key to solve. The public key infrastructure (PKI) is used to encrypt and decrypt emails. Each person is assigned a public and private key in the form of digital code.
The public key is stored on a key server along with the person’s name and email address, and can be accessed by anyone. This public key is what is used to encrypt the email. If someone wanted to send you an email with sensitive information, they would use your public key to encrypt it. The private key is used to decrypt emails. It is stored somewhere safe and private on the person’s computer and only that person has access to it. The private key can also be used to digitally “sign” a message so the recipient knows it came from you.
Why is Email Encryption Important?
Email encryption is important because it protects you from a data breach. If the hacker can’t read your message because it’s encrypted, they can’t do anything with the information. Since 2013, over 13 billion data records have been lost or stolen. The average cost of a data breach in 2018 is $3.86 million. This number has grown by 6.4% since 2017. Data breaches can be costly because they take a while to identify. In 2018, the mean time to identify a breach was 197 days and the mean time to contain it was 69 days. Email encryption is a preventative measure you can take to avoid being part of these statistics.
Types of Email Encryption
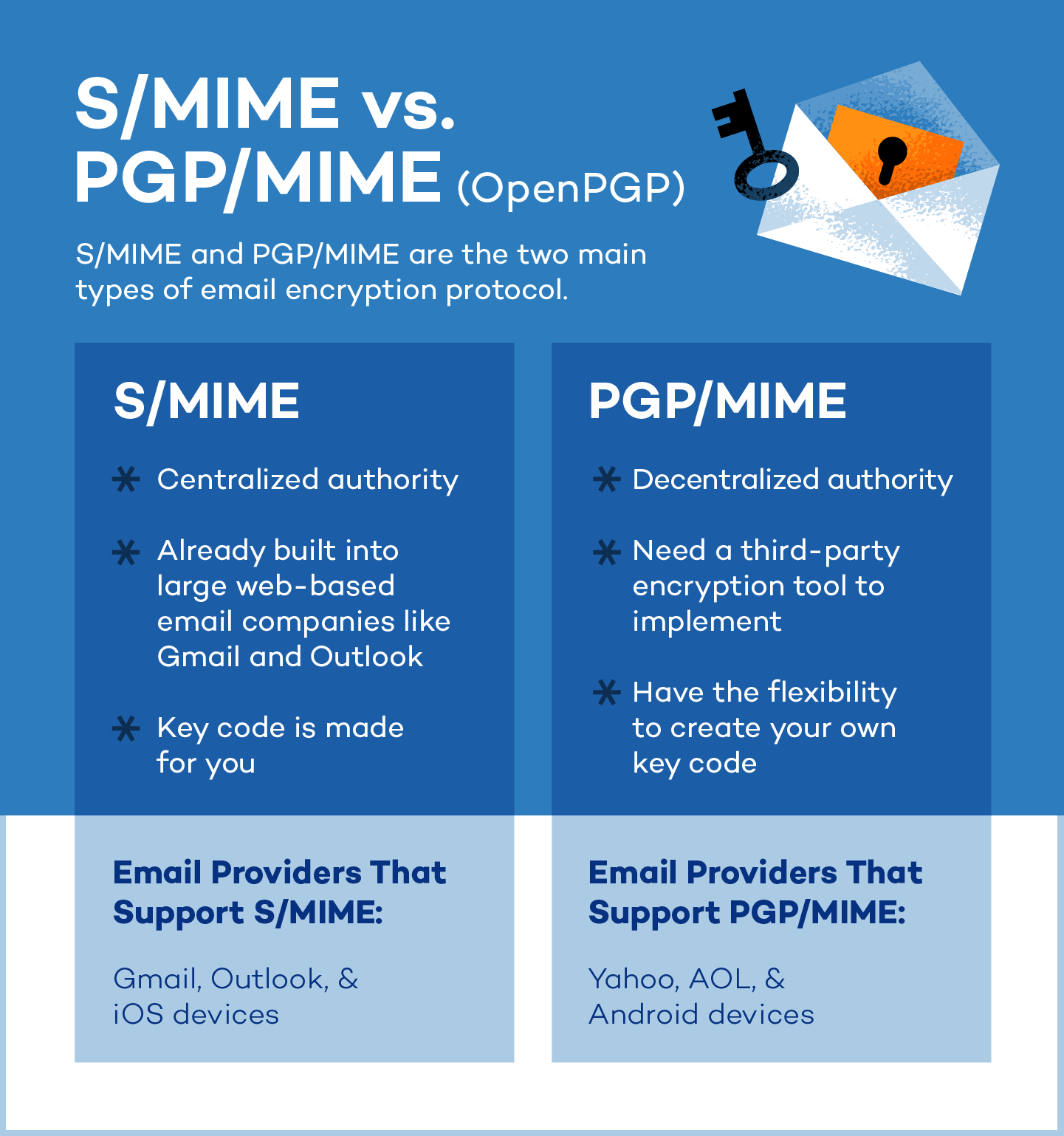 The two main types of email encryption protocol are S/MIME and PGP/MIME. S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) is built into most OSX and iOS devices and relies on a centralized authority to pick the encryption algorithm. S/MIME is used most often because it is built into large web-based email companies such as Apple and Outlook.
The two main types of email encryption protocol are S/MIME and PGP/MIME. S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) is built into most OSX and iOS devices and relies on a centralized authority to pick the encryption algorithm. S/MIME is used most often because it is built into large web-based email companies such as Apple and Outlook.
PGP/MIME (Pretty Good Privacy/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) relies on a decentralized trust model and was developed to address security issues facing plain text messages. Within this model, there is more flexibility and control over how well you want your emails to be encrypted, but it requires a third-party encryption tool.
How to Encrypt Emails in Gmail
 Gmail already has S/MIME built into the app, but it only works if both the sender and receiver have it enabled.
Gmail already has S/MIME built into the app, but it only works if both the sender and receiver have it enabled.
- Enable hosted S/MIME. You can enable this setting by following Google’s instructions on enabling hosted S/MIME.
- Compose your message as you normally would.
- Click on the lock icon to the right of the recipient.
- Click on “view details” to change the S/MIME settings or level of encryption.
When changing the encryption levels note these color codes:
Green — Information is protected by S/MIME encryption and can only be decrypted with a private key.
Gray — The email is protected with TLS (Transport Layer Security). This only works if both the sender and recipient have TLS capabilities.
Red — The email has no encryption security.
How to Encrypt Emails in Outlook
 Outlook is also compatible with the S/MIME protocol, but it requires additional setup.
Outlook is also compatible with the S/MIME protocol, but it requires additional setup.
- Enable S/MIME encryption. This process will involve getting a certificate or digital ID from your organization’s administrator and installing S/MIME control. Follow Office’s steps for setting up to use S/MIME encryption.
- Encrypt all messages or digitally sign all messages by going to the gear menu and clicking S/MIME settings. Choose to either encrypt contents and attachments of all messages or add a digital signature to all messages sent.
- Encrypt or remove individual messages by selecting more options (three dots) at the top of a message and choosing message options. Select or deselect “Encrypt this message (S/MIME).” If the person you are sending a message to doesn’t have S/MIME enabled, you’ll want to deselect the box or else they won’t be able to read your message.
How to Encrypt Emails on iOS
 iOS devices also have S/MIME support built in as a default.
iOS devices also have S/MIME support built in as a default.
- Go to advanced settings and switch S/MIME on.
- Change “Encrypt by Default” to yes.
- When you compose a message and lock icon will appear next to the recipient. Click the lock icon so it’s closed to encrypt the email.
Note: If the lock is blue, the email can be encrypted. If the lock is red, the recipient needs to turn on their S/MIME setting.
Email Providers That Need Third-Party Encryption Tools
 Email providers and devices that don’t have S/MIME compatibility built-in will need a third-party tool that allows them to use S/MIME or PGP/MIME protocol.
Email providers and devices that don’t have S/MIME compatibility built-in will need a third-party tool that allows them to use S/MIME or PGP/MIME protocol.
Encrypting Emails With Yahoo
Yahoo uses SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) as a layer of security to protect the account but requires third-party services to encrypt with S/MIME or PGP/MIME.
Encrypting Emails With Android
Android emails can be encrypted through S/MIME and PGP/MIME, but both require extra setup and a third-party app.
Encrypting Emails With AOL
Encrypting emails in AOL can be done manually, but requires a third-party tool to implement the PGP/MIME criteria. You first must download the PGP implementation and then obtain a program that allows you to use PGP encryption with your webmail provider.
Email Encryption Services
Email encryption can be done manually or by a secure email service. These email service apps each have unique offerings such as encrypting emails, attachments and contact lists. They do this in the background so you don’t have to worry about doing it manually.
Some notable providers are:
ProtonMail
ProtonMail allows you to enable end-to-end encryption and has PGP compatibility. It has different price levels, depending on the number of domains needed and messages sent per day.
Ciphermail
Ciphermail supports encryption through S/MIME, OpenPGP, TLS and PDF. It is popular for its compatibility with Android devices.
- Price: free
- Apps: Android
Mailvelope
Mailvelope is an OpenPGP encryption service for webmail. It’s compatible with Gmail, GMX, Outlook, Posteo, WEB.DE and Yahoo.
Virtru
Virtru provides end-to-end email encryption services and is compatible with Gmail, Outlook, Hotmail, Yahoo and a few other providers.
Startmail
Startmail supports encryption through PGP and is compatible with email services such as Outlook and Gmail.
- Price: free and paid plans
- Apps: none
Send 2.0
Sendinc offers military-grade encryption and is compatible with Outlook and Gmail.
- Price: free and paid plans
- Apps: Outlook plugin
Enlocked
Enlocked allows you to send and receive encrypted emails using PGP. It is compatible with Gmail, Yahoo, AOL, Microsoft and Outlook.
- Price: free and paid plans
- Apps: Chrome
Protect yourself and your business from cybersecurity threats by taking preventative measures. Implementing an advanced cybersecurity solution will help you find the best prevention techniques and instruct you on efficient ways to apply them to keep you safe from hackers.


